Chapter 13 - Motion and Time
Question and Answers
Question 1: Classify the following as motion along a straight line, circular or oscillatory motion:
(i) Motion of your hands while running. (Oscillatory Motion)
(ii) Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road. (Motion along a straight line)
(iii) Motion of a child in a merry-go-round. (Circular motion)
(iv) Motion of a child on a see-saw. (Oscillatory motion)
(v) Motion of the hammer of an electric bell. (Oscillatory motion)
(vi) Motion of a train on a straight bridge. (Motion along a straight line)
Question 2: Which of the following are not correct?
(i) The basic unit of time is second.
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
(iii) Distances between two cities are measured in kilometres.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
Answer: Incorrect statements:
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
Question 3: A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Answer:
Number of oscillations = 20
Time taken to complete 20 oscillations = 32 seconds
Time period = Number of oscillations/Time taken
= 32/20
= 1.6 seconds
Therefore, the time period of the simple pendulum is 1.6 seconds.
Question 4: The distance between two stations is 240 km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Answer:
Distance between two stations = 240 kilometre
Time taken to reach from station 1 to station 2 = 4 hours
Speed = Distance/Time
= 240/4
= 60 km/hr
Therefore, the speed of the train is 60 km/hr.
Question 5: The odometer of a car reads 57321.0 km when the clock shows the time 08:30 AM. What is the distance moved by the car, if at 08:50 AM, the odometer reading has changed to 57336.0 km? Calculate the speed of the car in km/min during this time. Express the speed in km/h also.
Answer:
Initial reading of the odometer = 57321.0 km
Final reading of the odometer = 57336.0 km
Distance covered by the car = Final reading of the odometer - Initial reading of the odometer
= 57336.0 - 57321.0 = 15 km
Starting time = 08:30 AM
Ending time = 08:50 AM
Time taken to complete 15 km = Starting time - Ending time
= 08:50 - 08:30 = 20 minutes
(Speed of car in km/min)
Speed = Distance/Time
= 15/20
= 3/4 km/min
(Speed of car in km/hr)
1 hour = 60 minutes
20 minutes = 1/6 x 20
= 1/3 hr
Speed = Distance/Time
= 15/1/3 km/hr
Therefore, the speed of car in km/min is 3/4 km/min and the speed of the car in km/hr is 15/1/3 km/hr.
Question 6: Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Answer:
Time taken by Salma to reach school from home = 15 minutes
Speed of bicycle = 2 m/s
Distance between her school and her home = ?
15 minutes = _____ seconds
= 15 x 60
= 900 seconds
Distance = Speed x Time
= 2 x 900
= 1800 m
1800 m = ________ km
= 1800/1000
= 1.8 km
Therefore, the distance between her house and her home is 1.8 km.
Question 7: Show the shape of the distance - time graph for the motion in the following cases:
(i) A car moving with a constant speed.
(ii) A car parked on a side road.
Answer:
(i)
(ii)
Question 8: Which of the following relations is correct?
(i) Speed = Distance × Time
(ii) Speed = Distance/Time
(iii) Speed = Time/Distance
(iv) Speed = 1/Distance x Time
Answer: (ii) Speed = Distance/Time
9. The basic unit of speed is:
(i) km/min
(ii) m/min
(iii) km/h
(iv) m/s
Answer: (iv) m/s
Question 10: A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is:
(i) 100 km
(ii) 25 km
(iii) 15 km
(iv) 10 km
Answer: (ii) 25 km
(When the speed of the car is 40 km/hr)
Time taken = 15 min (15/60 = 1/4 hr)
Speed = Distance/Time
Distance covered = speed x time taken
= 40 x 1/4 = 10 km
(When the speed of the Car is 60 km/ h)
Speed = Distance/Time
Distance covered = speed x time taken
= 60 x 1/4= 15 km
Total distance covered by the car = 10 + 15 = 25 km
Question 11: Suppose the two photographs, shown in Fig. 13.1 and Fig. 13.2, had been taken at an interval of 10 seconds. If a distance of 100 metres is shown by 1 cm in these photographs, calculate the speed of the fastest car.
Answer:
The distance covered by the blue car (as evident from the photograph) from one horizontal white strip to another, which is measured by scale is 1.2 cm.
Given that 1 cm is equivalent to 100 m. Therefore, 1.2 cm is equivalent to 120 m.
Distance travelled by the car = 120 m
Time taken to cover this distance = Time interval between the two photographs = 10 s
Speed = Distance/Time
= 120/10
= 12 m/s
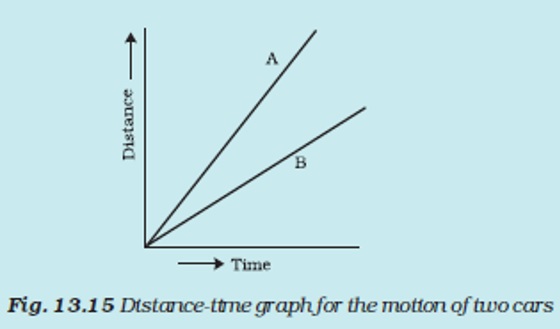
Question 12: Fig. 13.15 shows the distance-time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?
Answer: Vehicle A is moving faster than vehicle B.
Question 13: Which of the following distance-time graphs shows a truck moving with speed which is not constant?
Answer: (iii)




Hello! This is Ram... Hope you're doing well... I actually like your blog... You help me by posting different notes of different subjects! Your blog is advanced! But could you please add bell icon of subscribe button to your blog so that we could be notified what ever you post...
ReplyDeleteSo it is my kind request to add subscribe button to your blog....
Thank you!
Warm regards,
Ram
Hello! I've just shared this post with my friend
ReplyDelete