Chapter 13 - Motion and Time Notes
1. Motion is a change in position of an object with respect to time.
If the position of a body is not changing with respect to time, the body
is said to be at rest. Any moving body is said to be in motion.
2. Some types of motion are:
• Straight line motion
• Circular motion
• Oscillatory motion
3.
Straight line motion - Motion in a straight line is called rectilinear
motion. In other words, when an object moves along a straight line path,
it is called rectilinear motion. Example: The motion of a bullock cart
moving on a straight road, motion of a horse pulling a cart on a
straight road, motion of a train on a straight bridge etc.
4.
Circular motion - A round path having the shape of a circle is called
circular path. When an object moves along a circular path, it is called
circular motion. Example: The earth moves around the sun in a circular
path, motion of a child in a merry-go-round, motion of pedals of a
moving bicycle etc.
5. Oscillatory motion - The to and fro motion
of a simple pendulum is an example of a periodic or an oscillatory
motion. Example: Oscillation of simple pendulum
6. Speed is
defined as the rate of change of position of an object in any direction.
Speed is measured as the ratio of distance to the time in which the
distance was covered. Speed is a scalar quantity.
7. Speed = Total distance covered/Total time taken
8.
If the speed of an object moving along a straight line keeps changing,
its motion is said to be non-uniform. On the other hand, an object
moving along a straight line with a constant speed is said to be in
uniform motion.
9. Well - known periodic motions is that of a simple pendulum.
10.
A simple pendulum consists of a small metallic ball or a piece of stone
suspended from a rigid stand by a thread. The metallic ball is called
the bob of the pendulum. When the bob of the pendulum is released after
taking it slightly to one side, it begins to move to and fro. The to and
fro motion of a simple pendulum is an example of a periodic or an
oscillatory motion.
11. The pendulum is said to have completed
one oscillation when its bob, starting from its mean position O, moves
to A, to B and back to O. The pendulum also completes one oscillation
when its bob moves from one extreme position A to the other extreme
position B and comes back to A. The time taken by the pendulum to
complete one oscillation is called its time period.

12. Time period = Number of oscillations/Time taken
13. The basic unit of time is a second. Its symbol is s. Larger units of time are minutes (min) and hours (h).
14. The basic unit of speed is distance/time, while the basic unit of speed is m/s.
15. Distance covered = Speed × Time
16. Time taken = Distance/Speed
17. The meter that measures the distance moved by the vehicle is called an odometer.
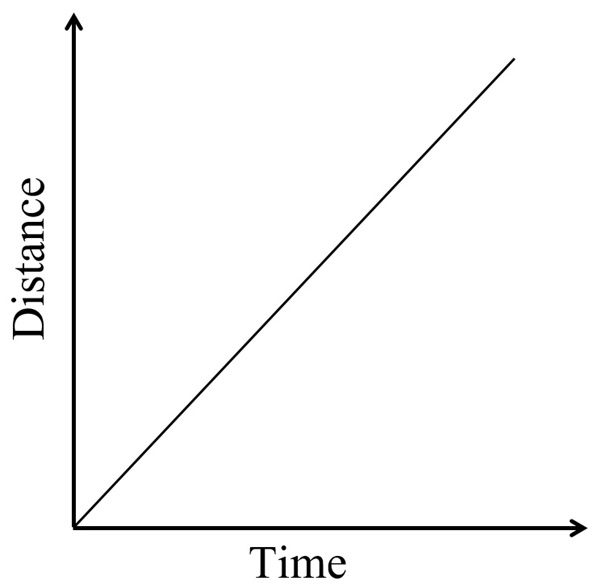
18. Distance - Time graph
i) An object moving with a constant speed
ii) An object moving parked
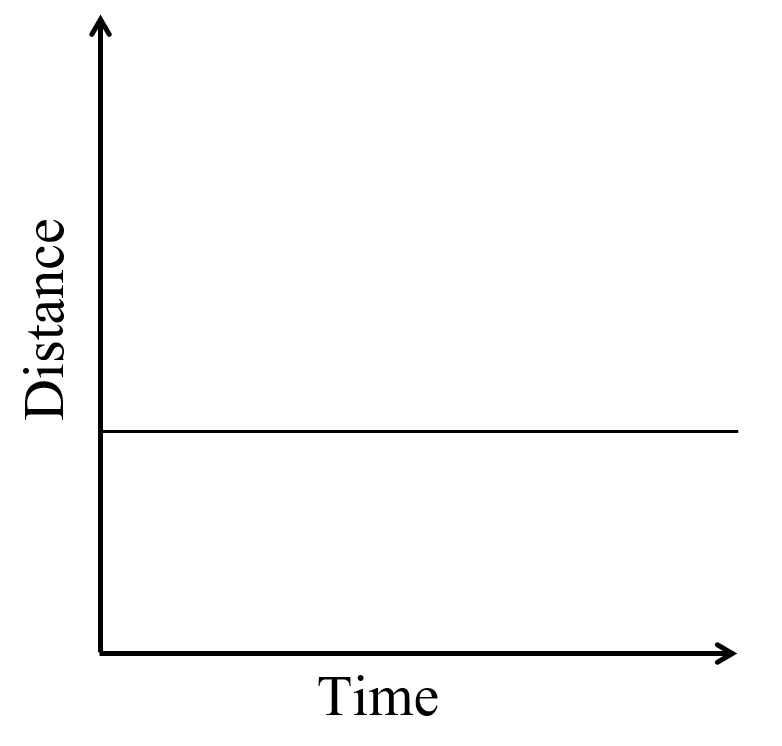
19.
There is an interesting story about the discovery that the time period
of a given pendulum is constant. It is said that once Galileo was
sitting in a church. He noticed that a lamp suspended from the ceiling
with a chain was moving slowly from one side to the other. He was
surprised to find that his pulse beat the same number of times during
the interval in which the lamp completed one oscillation. Galileo
experimented with various pendulums to verify his observation. He found
that a pendulum of a given length takes always the same time to complete
one oscillation. This observation led to the development of pendulum
clocks. Winding clocks and wristwatches were refinements of the pendulum
clocks.
20. One microsecond is one millionth of a second. A nanosecond is one billionth of a second.
No comments:
Post a Comment