Chapter 9 - Reproduction in Animals
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1: Sets of reproductive terms are given below. Choose the set that has an incorrect combination.
a) sperm, testis, sperm duct, penis
b) menstruation, egg, oviduct, uterus
c) sperm, oviduct, egg, uterus
d) ovulation, egg, oviduct, uterus
Answer: c) sperm, oviduct, egg, uterus
Question 2: In humans, the development of fertilised egg takes place in the
a) ovary
b) testis
c) oviduct
d) uterus
Answer: d) uterus
Question 3: In the list of animals given below, hen is the odd one out.
human being, cow, dog, hen
The reason for this is
a) it undergoes internal fertilisation.
b) it is oviparous.
c) it is viviparous.
d) it undergoes external fertilisation.
Answer: b) it is oviparous.
Question 4: Animals exhibiting external fertilisation produce a large number of gametes. Pick the appropriate reason from the following.
a) The animals are small in size and want to produce more offsprings.
b) Food is available in plenty in water.
c) To ensure better chance of fertilisation.
d) Water promotes production of large number of gametes.
Answer: c) To ensure better chance of fertilisation.
Question 5: Reproduction by budding takes place in
a) hydra
b) amoeba
c) paramecium
d) bacteria
Answer: a) hydra
Question 6: Which of the following statements about reproduction in humans is correct?
a) Fertilisation takes place externally.
b) Fertilisation takes place in the testes.
c) During fertilisation egg moves towards the sperm.
d) Fertilisation takes place in the human female.
Answer: d) Fertilisation takes place in the human female.
Question 7: In human beings, after fertilisation, the structure which gets embedded in the wall of uterus is
a) ovum
b) embryo
c) foetus
d) zygote
Answer: b) embryo
Question 8: Aquatic animals in which fertilisation occurs in water are said to be:
a) viviparous without fertilisation.
b) oviparous with external fertilisation.
c) viviparous with internal fertilisation.
d) oviparous with internal fertilisation.
Answer: b) oviparous with external fertilisation.
Question 9: After fertilisation, the resulting cell which gives rise to a new individual is the
a) embryo
b) ovum
c) foetus
d) zygote
Answer: d) zygote
Question 10: In human beings, the correct sequence of events during reproduction is
a) gamete formation, fertilisation, zygote, embryo
b) embryo, zygote, fertilisation, gamete formation
c) fertilisation, gamete formation, embryo, zygote
d) gamete formation, fertilisation, embryo, zygote
Answer: a) gamete formation, fertilisation, zygote, embryo
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 11: Although 2 cells called gametes fuse, the product formed is a single cell called zygote. Justify.
Answer: During fertilisation, only the nucleus of the sperm moves into the egg cell and fuses with the egg nucleus to form the zygote. The sperm degenerates.
Question 12: Stages in the lifecycle of silkworm are given below. Write them in sequential order.
pupa, silkworm, egg, silkmoth
Answer: The sequential order in stages in the lifecycle of silkworm is Egg, Pupa, Silkmoth, Silkworm.
Question 13: What is the importance of reproduction?
Answer: Reproduction is important because without it, a species wouldn’t survive over time. Individuals must reproduce to ensure that they will continue on over generation of time.
Question 14: In markets, eggs of birds are available but never eggs of dogs. Why?
Answer: The animals which lay the eggs are called oviparous animals and birds are oviparous. The animal which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals and dogs are viviparous. Therefore, dogs don’t lay eggs.
Question 15: The eggs of frogs do not have shells for protection, yet they are safe in water. How?
Answer: The eggs of frogs do not have shells for protection, yet they are safe in water because a layer of jelly holds the eggs together and provides protection to the eggs.
Short Answer Questions
Question 16: Fill up the blanks with the terms given below:
body, asexual, binary, single, nucleus
Amoeba is a ___________ celled organism. It reproduces by ___________ reproduction. The process of reproduction begins by the division of its ___________ into two. This is followed by the division of its ___________ into two. This type of reproduction is called ___________ fission.
Answer:
Amoeba is a single celled organism. It reproduces by asexual reproduction. The process of reproduction begins by the division of its nucleus into two. This is followed by the division of its body into two. This type of reproduction is called binary fission.
Question 17: The term metamorphosis is not used while describing human development. Why?
Answer: The term metamorphosis is not used while describing human development. This is because in human beings, body parts of an adult are present from the time of birth itself. While, in metamorphosis, the parts of the adult are different from those at the time of birth.
Question 18: Mother gives birth to a baby but the baby has characters of both parents. How is this possible?
Answer: Mother gives birth to a baby but the baby has the characters of both the parents because fertilisation involves two gametes, one from the mother and the other from father. The zygote, therefore has both father and mother’s contribution. Since the zygote develops into the baby it has characters of both parents.
Question 19: How is reproduction in hydra different from that in amoeba?
Answer: In each hydra, there may be one or more bulges. These bulges are the developing new individuals and they are called buds. In hydra too the new individuals develop as outgrowths from a single parent. This type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction. Since new individuals develop from the buds in hydra, this type of asexual reproduction is called budding.
Amoeba is a single-celled organism. It begins the process of reproduction by the division of its nucleus into two nuclei. This is followed by division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus. Finally, two amoebae are produced from one parent amoeba. This type of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is called binary fission.
Question 20: State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct the statement:
a) External fertilisation can occur both in water and on land.
b) The eggs of fish are covered by hard shells for protection.
c) Human egg has a head, middle piece and tail.
d) In adult human females, a single mature egg is released into an oviduct every month.
Answer:
a) False; External fertilisation occurs only in water.
b) False; The eggs of fish are covered by a jelly for protection.
c) False; Human sperm has a head, middle piece and tail.
d) True
Question 21: Why do only male gametes have a tail?
Answer: Male gametes (sperms) are motile. The tail helps the sperm to swim through the reproductive tract of the female to reach the oviduct. The sperms are produced within the male reproductive system. Sperms are small unicellular structures with a head, middle piece, and a tail.
Question 22: What does Fig. 9.1 represent?

Answer: The figure shows an amoeba undergoing binary fissions with a dividing nucleus.
Question 23: Observe the figure given as Fig. 9.2 and answer the questions that follow.
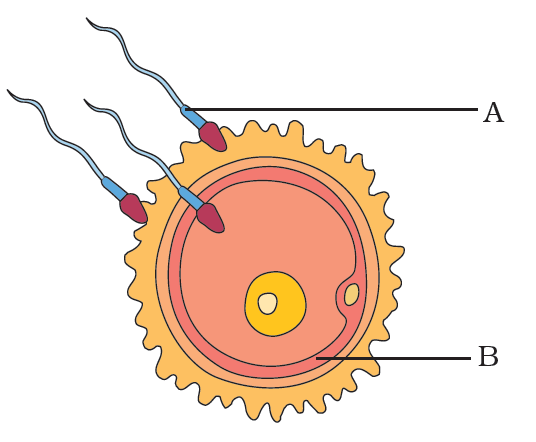
a) Label A and B.
b) Identify the process.
c) What happens during this process and what is formed?
Answer:
a) A is sperms. B is Ovum or the egg.
b) The process is fertilization. The fusion of the genetic material contained in the gametes to form a zygote is called fertilization.
Long Answer Questions
Question 24: How can we say that fish exhibits external fertilisation?
Answer: The female release eggs, the male deposits sperms over them. Each sperm swims randomly in water with the help of its long tail. The sperms come in contact with the eggs. This results in fertilisation. This type of fertilisation in which the fusion of a male and a female gamete takes place outside the body of the female is called external fertilisation.
Question 25:
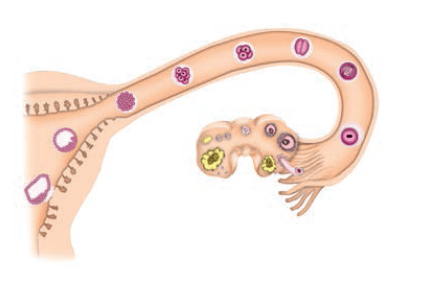
After observing Fig. 9.3 answer the following.
a. Read the following statements and label them in the figure:
i) The part which produces female gametes.
ii) The part where development of the baby takes place.
iii) The part through which the developing embryo passes to reach the uterus.
b. Explain the future development of the embryo that would take place after it gets embedded in the uterus.
Answer:
a.
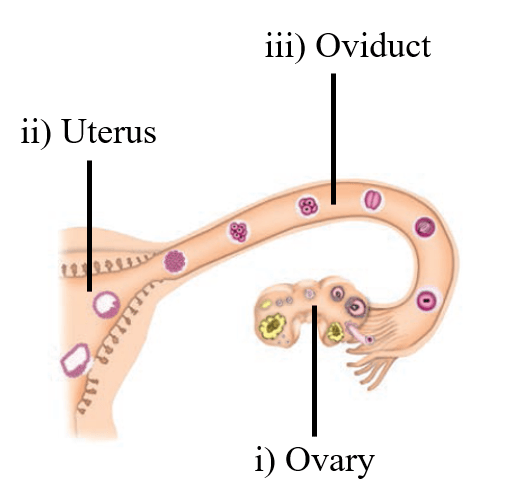
b. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells. The cells then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is termed an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, ears etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus. When the development of the foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Question 26: Hens and frogs are both oviparous exhibiting different types of fertilisation. Explain.
Answer: Hens and frogs are both oviparous exhibiting different types of fertilization. This is because hens follow internal fertilization while the frogs follow external fertilization. Internal fertilization is a fertilization which takes place inside the body of the female while External fertilization is a fertilization which takes place outside the body.
Question 27: Observe the following figures.
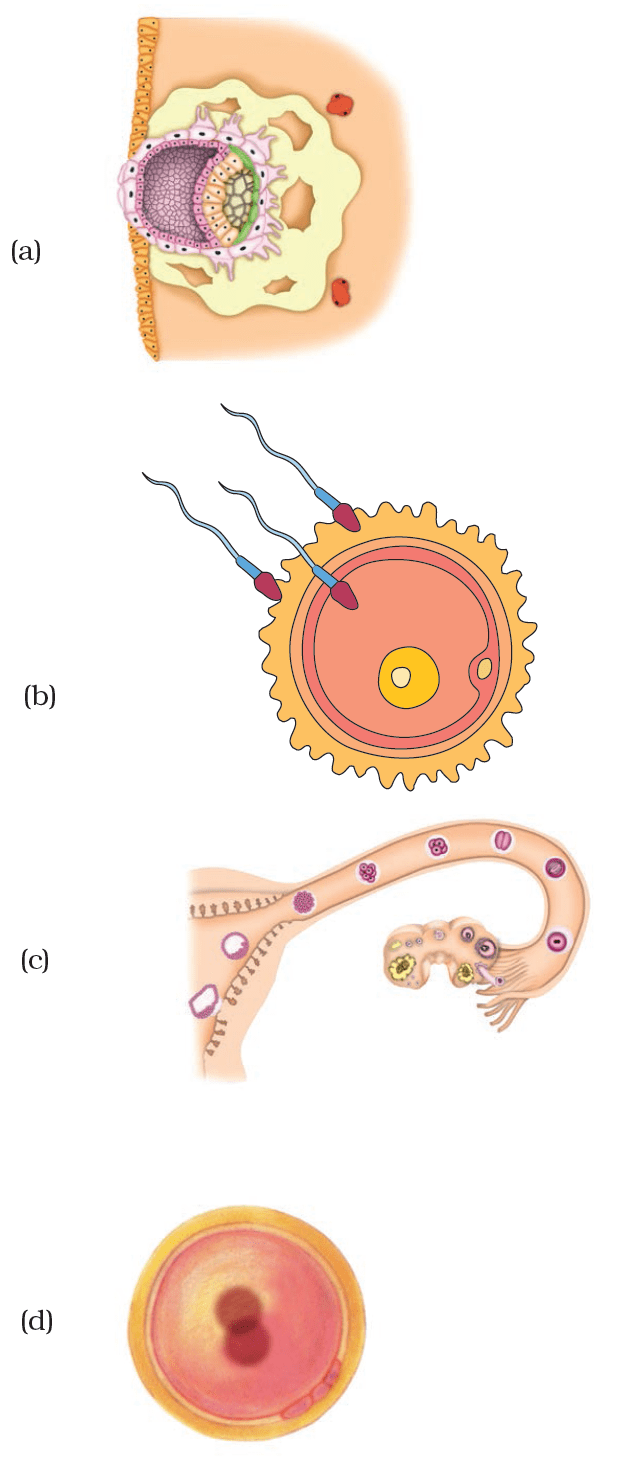
i) Identify the stages a to d in Fig. 9.4 during development of human baby.
ii) Arrange the stages in correct sequence of development.
iii) Explain the development that takes place in any one stage.
Answer:
i)
a) Embedding of the embryo in the uterus.
b) Fertilisation.
c) Zygote formation and development of an embryo from the zygote.
d) Zygote showing fusion of nuclei.
ii) The correct sequence is c, b, d, a.
iii) Development of Embryo
Fertilisation results in the formation of zygote which begins to develop into an embryo. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells. The cells then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is termed an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, ears etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus.
No comments:
Post a Comment