Chapter 13 - Sound Extra Questions
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. The voice box is also called as
a) stomach
b) heart
c) larynx
d) mouth
Answer: c) larynx
2. Sound is a kind of
a) work
b) energy
c) force
d) pressure
Answer: b) energy
3. The hearing range of human ear is
a) 20 Hz to 20000 Hz
b) less than 20 Hz
c) more than 20000 Hz
d) 20 Hz to 25000 Hz
Answer: a) 20 Hz to 20000 Hz
4. Pitch of a sound is determined by its
a) frequency
b) speed
c) amplitude
d) loudness
Answer: a) frequency
5. The frequency of supersonic sound is
a) more than 20 Hz
b) 100 Hz
c) less than 20 Hz
d) more than 20000 Hz
Answer: d) more than 20000 Hz
6. Cochlea is a part of
a) hearing organ
b) sound producing organ
c) muscular organ
d) air pollution
Answer: a) hearing organ
7. 1 Hertz is equal to
a) 1 vibration per minute
b) 10 vibration per second
c) 60 vibrations per minute
d) 600 vibrations per minute
Answer: c) 60 vibrations per minute
8. Sound can’t travel through
a) air
b) water
c) air
d) vacuum
Answer: d) vacuum
9. The sound in the audible range is called
a) ultrasonic sound
b) sonic sound
c) supersonic sound
d) light sound
Answer: b) sonic sound
10. Speed is
a) Distance travelled by time
b) Time distance travelled
c) Distance travelled × time
d) Time + distance travelled
Answer: a) Distance travelled by time
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s
11. In human beings, sound is produced by _______________________.
12. Sound of frequency lower than 20 Hz is called the ___________________________.
13. The ___________ nerve is also present in the inner ear.
14. Sounds which are unpleasant to the ear is called __________.
15. Too much noise in our surroundings that causes discomfort is called _________________.
16. The speed of sound is maximum in __________.
17. Sounds of frequencies higher than 20000 Hz are called _______________ sounds.
18. _______ is the time taken by a vibrating body for one complete vibration.
19. Above ___________ the noise becomes physically painful.
20. Plantations on roadside can reduce _________________.
Answer:
11. In human beings, sound is produced by larynx or the voice box.
12. Sound of frequency lower than 20 Hz is called the infrasonic sounds.
13. The auditory nerve is also present in the inner ear.
14. Sounds which are unpleasant to the ear is called noise.
15. Too much noise in our surroundings that causes discomfort is called noise pollution.
16. The speed of sound is maximum in solids.
17. Sounds of frequencies higher than 20000 Hz are called ultrasonic sounds.
18. Time period is the time taken by a vibrating body for one complete vibration.
19. Above 80 dB (80 Decibels) the noise becomes physically painful.
20. Plantations on roadside can reduce noise pollution.
Match the following

Answer:
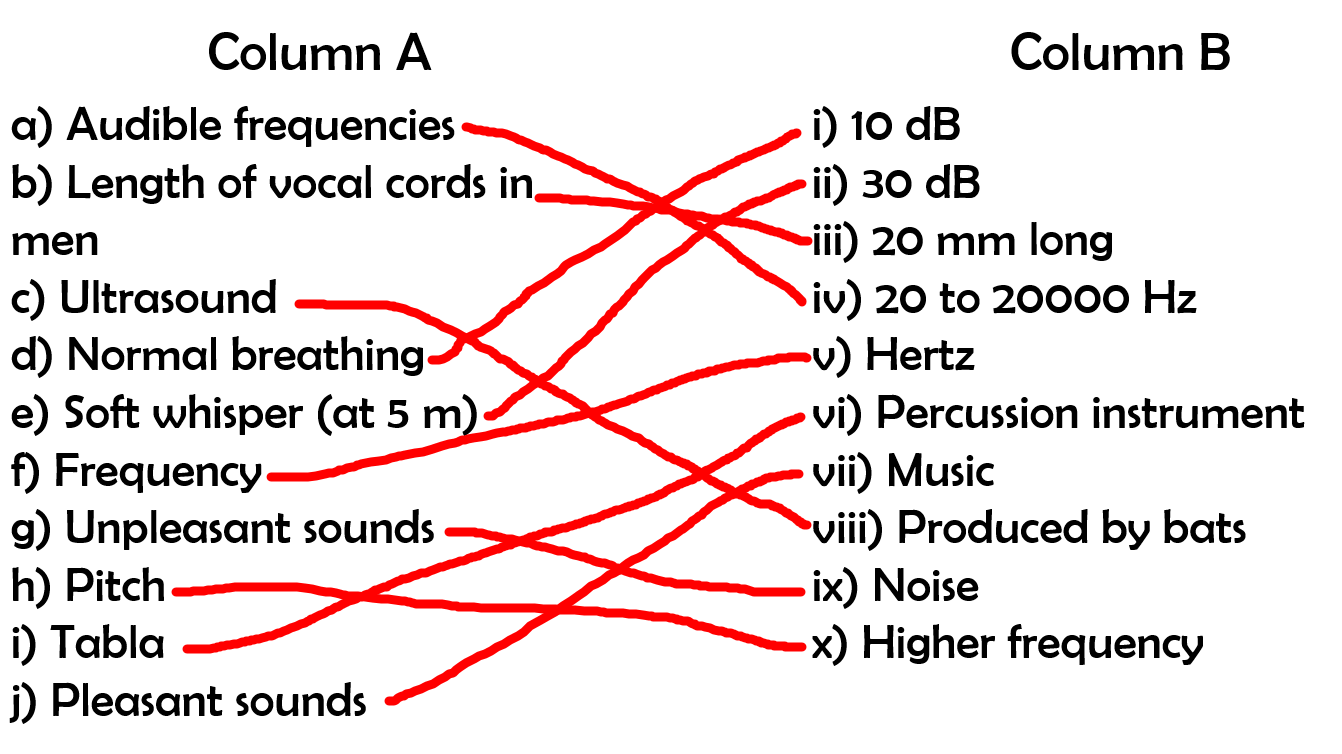
True or False
21. All human beings can hear sounds of frequencies up to 60000 Hz.
22. The sound in sitar is produced by plucking its strings.
23. Sound can’t travel through vacuum.
24. Sound doesn’t need a medium for its propagation.
25. The loudness of the sound is expressed in a unit called decibel.
26. Loud sound have higher frequencies.
27. Sound travels faster in air, slower in iron.
28. Light travels much faster than sound.
29. Man can’t hear sounds of bats.
30. The time taken to complete one oscillation is called frequency.
Answer:
21. False
22. True
23. True
24. False
25. True
26. False
27. False
28. True
29. True
30. False
Answer the following questions:
31. Write the differences between
a) supersonic and ultrasonic sounds
b) frequency and amplitude
c) music and noise
Answer:
a) Ultrasonic is used for ultrasound waves and is defined as waves with frequency more than 20 kHz. They cannot be heard by human beings. Supersonic is used for objects which travel at a speed greater than the speed of sound.
b) Frequency is the number of times the object vibrates per second. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). Amplitude is the maximum displacement of an object from its mean position. Amplitude is measured in metres (m), etc.
c) Music is a type of sound which is pleasant to hear. Noise is a type of sound which is unpleasant to hear.
32. Expand
a) SONAR
b) RADAR
Answer:
a) SONAR stands for Sound Navigation and Ranging. It is technique that is used for determining the distance and direction of underwater objects with the help of sound waves.
b) RADAR stands for Radio Detection and Ranging. It is detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance, angle or velocity of an object. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, vehicles, weather and terrain etc.
33. Give one word for the following.
a) Sounds that dogs can hear but humans can't.
b) Sound of a plane passing the speed of sound.
c) Sound with a frequency range of 20 - 20000 Hz.
d) Repetition of the sound waves after bouncing of large surface.
e) When different pitches combined in a rhythm.
Answer:
a) Ultrasonic sounds
b) Supersonic sounds
c) Audible Sounds
d) Echo
e) Music
34. Define the following
a) Frequency
b) Noise
c) Amplitude
d) Pitch
e) Loudness
Answer:
a) The number of times the object vibrates per second is called frequency.
b) Noise is a type of sound which is unpleasant to hear.
c) Maximum displacement of an object from its mean position is called amplitude.
d) Pitch is the highest or lowest sound, an object makes.
e) Loudness refers to how loud or soft a sound seems to a listener.
No comments:
Post a Comment