Chapter 3 - Mineral and Power Resources Notes
1. Mineral
• A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is a mineral.
• Minerals are not evenly distributed over space. They are concentrated in a particular area or rock formations.
• Some minerals are found in areas which are not easily accessible such as Arctic Ocean bed and Antarctica.
• Minerals are formed in different types of geological environments, under varying conditions. They are created by natural processes without any human interference.
• They can be identified on the basis of their physical properties such as colour, density, hardness and chemical property such as solubility.
2. Types of Minerals
On the basis of composition, minerals are classified mainly as metallic and non-metallic minerals.

• Metallic minerals contain metal in raw form. Metals are hard substances that conduct heat and electricity and have a characteristic lustre or shine. Iron ore, bauxite, manganese ore are some examples. Metallic minerals may be ferrous or non-ferrous.
→ Ferrous minerals like iron ore, manganese and chromites contain iron.
→ A non-ferrous mineral does not contain iron but may contain some other metal such as gold, silver, copper or lead.
• Non-metallic minerals do not contain metals. Limestone, mica and gypsum are examples of such minerals. The mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are also non-metallic minerals. Minerals can be extracted by mining, drilling or quarrying.
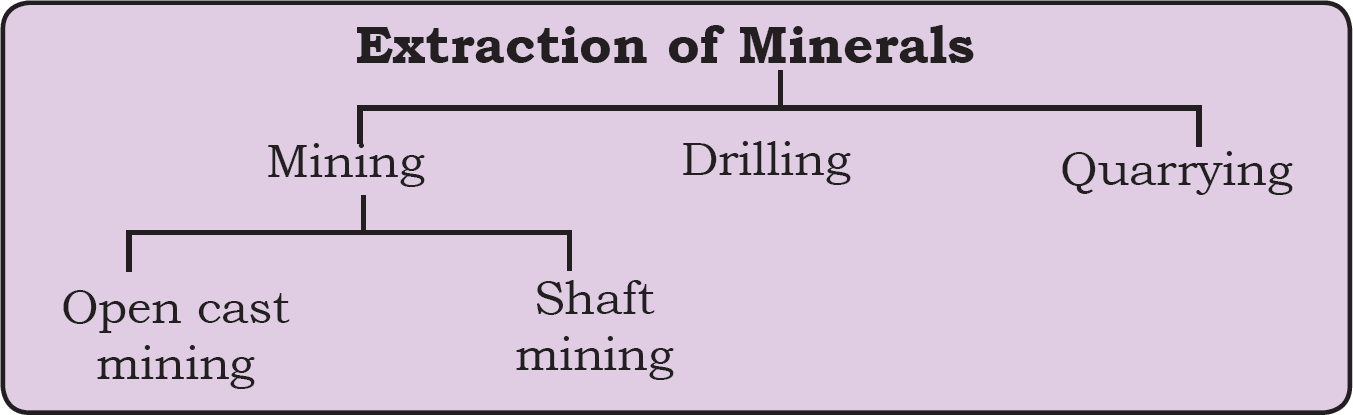
• The process of taking out minerals from rocks buried under the earth’s surface is called mining.
• Minerals that lie at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer; this is known as open-cast mining. Deep bores, called shafts, have to be made to reach mineral deposits that lie at great depths. This is called shaft mining.
• Petroleum and natural gas occur far below the earth’s surface. Deep wells are bored to take them out, this is called drilling. Minerals that lie near the surface are simply dug out, by the process known as quarrying.
3. Distribution of Minerals
• Minerals occur in different types of rocks. Some are found in igneous rocks, some in metamorphic rocks while others occur in sedimentary rocks.
• Generally, metallic minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rock formations that form large plateaus. Iron-ore in north Sweden, copper and nickel deposits in Ontario, Canada, iron, nickel, chromites and platinum in South Africa are examples of minerals found in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
• Sedimentary rock formations of plains and young fold mountains contain non-metallic minerals like limestone. Limestone deposits of Caucasus region of France, manganese deposits of Georgia and Ukraine and phosphate beds of Algeria are some examples.
• Mineral fuels such as coal and petroleum are also found in the sedimentary strata.
4. Mineral Distribution in Asia
• China and India have large iron ore deposits.
• Asia produces more than half of the world’s tin.
• China, Malaysia and Indonesia are among the world’s leading tin producers.
• China also leads in production of lead, antimony and tungsten.
• Asia also has deposits of manganese, bauxite, nickel, zinc and copper.
5. Mineral Distribution in Europe
• Europe is the leading producer of iron-ore in the world.
• The countries with large deposits of iron ore are Russia, Ukraine, Sweden and France.
• Minerals deposits of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel are found in Eastern Europe and European Russia.
6. Mineral Distribution in North America
• The mineral deposits in North America are located in three zones: the Canadian region north of the Great Lakes, the Appalachian region and the mountain ranges of the west.
• Iron ore, nickel, gold, uranium and copper are mined in the Canadian Shield Region, coal in the Appalachians region. Western Cordilleras have vast deposits of copper, lead, zinc, gold and silver.
7. Mineral Distribution in South America
• Brazil is the largest producer of high grade iron-ore in the world.
• Chile and Peru are leading producers of copper.
• Brazil and Bolivia are among the world’s largest producers of tin.
• South America also has large deposits of gold, silver, zinc, chromium, manganese, bauxite, mica, platinum, asbestos and diamond.
• Mineral oil is found in Venezuela, Argentina, Chile, Peru and Columbia.
8. Mineral Distribution in Africa
• Africa is the world’s largest producer of diamonds, gold and platinum.
• South Africa, Zimbabwe and Zaire produce a large portion of the world’s gold.
• The other minerals found in Africa are copper, iron ore, chromium, uranium, cobalt and bauxite.
• Oil is found in Nigeria, Libya and Angola.
9. Mineral Distribution in Australia
• Australia is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
• It is a leading producer of gold, diamond, iron ore, tin and nickel.
• It is also rich in copper, lead, zinc and manganese.
• Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie areas of Western Australia have the largest deposits of gold.
10. Mineral Distribution in Antarctica
• The geology of Antarctica is sufficiently well known to predict the existence of a variety of mineral deposits, some probably large.
• Significant size of deposits of coal in the Transantarctic Mountains and iron near the Prince Charles Mountains of East Antarctica is forecasted.
• Iron ore, gold, silver and oil are also present in commercial quantities.
11. Uses of Minerals
Minerals are used in many industries.
• Minerals which are used for gems are usually hard. These are then set in various styles for jewellery.
• Copper is another metal used in everything from coins to pipes.
• Silicon, used in the computer industry is obtained from quartz.
• Aluminium obtained from its ore bauxite is used in automobiles and airplanes, bottling industry, buildings and even in kitchen cookware.
12. Conservation of Minerals
• Minerals are a non-renewable resource.
• It takes thousands of years for the formation and concentration of minerals.
• The rate of formation is much smaller than the rate at which the humans consume these minerals. It is necessary to reduce wastage in the process of mining.
• Recycling of metals is another way in which the mineral resources can be conserved.
13. Power Resources
Power or energy plays a vital role in our lives. We also need power for industry, agriculture, transport, communication and defense. Power resources may be broadly categorised as conventional and non-conventional resources.
• Conventional Sources: Conventional sources of energy are those which have been in common use for a long time. Firewood and fossil fuels are the two main conventional energy sources.
→ Firewood
*It is widely used for cooking and heating. In India, more than 50% of the energy used by villagers comes from fire wood.
*Remains of plants and animals which were buried under the earth for millions of years got converted by the heat and pressure into fossil fuels.
*Fossil fuel such as coal, petroleum and natural gas are the main sources of conventional energy. The reserves of these minerals are limited. The rate at which the growing world population is consuming them is far greater than the rate of their formation. So, these are likely to be exhausted soon.
→ Coal
*This is the most abundantly found fossil fuel.
*It is used as a domestic fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines and to generate electricity. Electricity from coal is called thermal power.
*The coal which we are using today was formed millions of years ago when giant ferns and swamps got buried under the layers of earth. Coal is therefore referred to as Buried Sunshine.
*The leading coal producers of the world are China, USA, Germany, Russia, South Africa and France.
*The coal producing areas of India are Raniganj, Jharia, Dhanbad and Bokaro in Jharkhand.
→ Petroleum
*It is found between the layers of rocks and is drilled from oil fields located in off-shore and coastal areas. This is then sent to refineries which process the crude oil and produce a variety of products like diesel, petrol, kerosene, wax, plastics and lubricants.
*Petroleum and its derivatives are called Black Gold as they are very valuable.
*The chief petroleum producing countries are Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Qatar. The other major producers are USA, Russia, Venezuela, and Algeria.
*The leading producers in India are Digboi in Assam, Bombay High in Mumbai and the deltas of Krishna and Godavari rivers.
→ Natural Gas
*Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits and is released when crude oil is brought to the surface. It can be used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
*Russia, Norway, UK and the Netherlands are the major producers of natural gas.
*In India Jaisalmer, Krishna Godavari delta, Tripura and some areas off shore in Mumbai have natural gas resources.
→ Hydel Power
*Rain water (river water) stored in dams is made to fall from heights. The falling water flows through pipes inside the dam over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam.
*The moving blades then turn the generator to produce electricity. This is called hydro-electricity.
*The water discharged after the generation of electricity is used for irrigation.
*One fourth of the world’s electricity is produced by hydel power.
*The leading producers of hydel power in the world are Paraguay, Norway, Brazil, and China.
*Some important hydel power stations in India are Bhakra Nangal, Gandhi Sagar, Nagarjunsagar and Damodar valley projects.
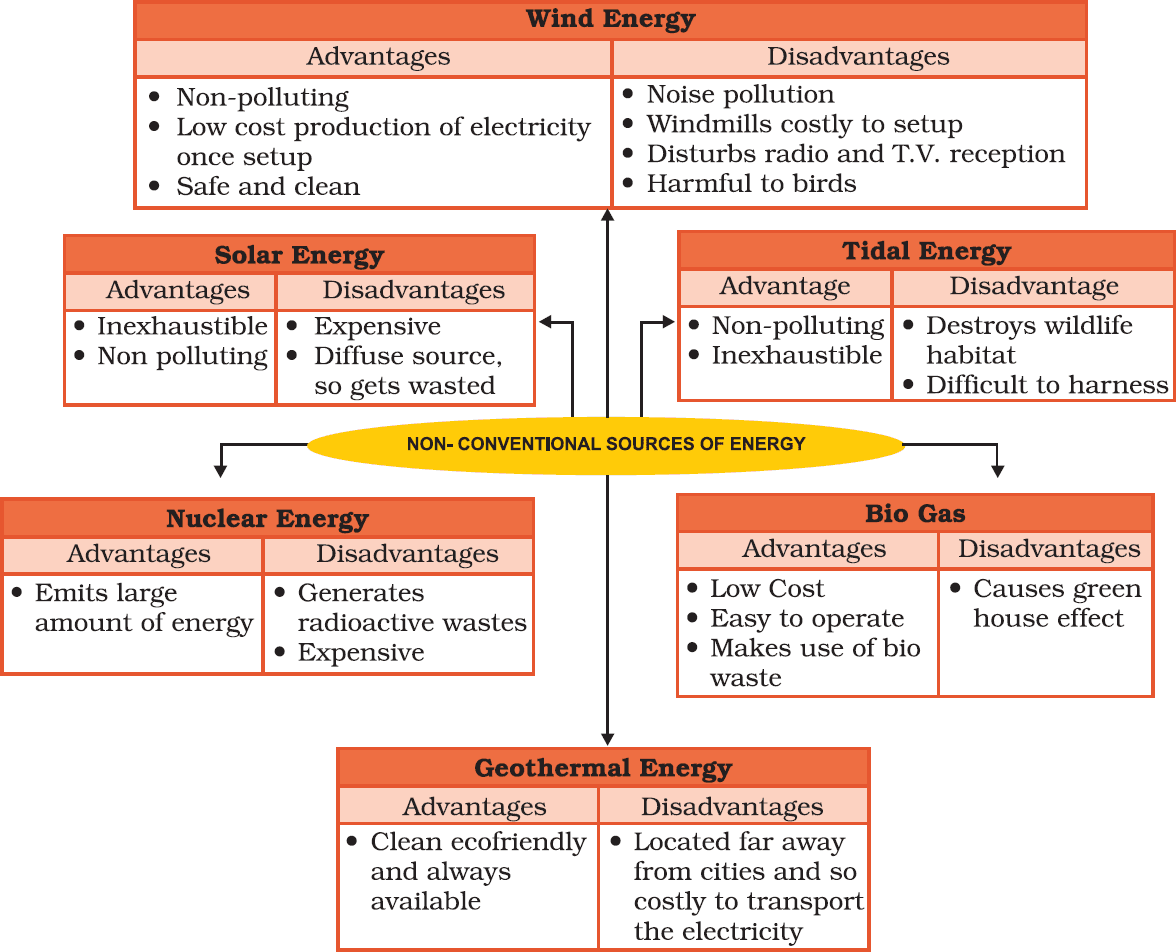
• Non-conventional resources
The increasing use of fossil fuels is leading to its shortage. It is estimated that if the present rate of consumption continues, the reserves of these fuel will get exhausted. Moreover, their use also causes environmental pollution. Therefore, there is need for using non-conventional sources such as solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy which are renewable.
→ Solar energy
*Solar energy trapped from the sun can be used in solar cells to produce electricity.
*Many of these cells are joined into solar panels to generate power for heating and lighting purpose.
*Solar energy is also used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers besides being used for community lighting and traffic signals.
→ Wind energy
*Wind is an inexhaustible source of energy. Wind mills have been used for grinding grain and lifting water since times immemorial.
*In modern time wind mills, the high speed winds rotate the wind mill which is connected to a generator to produce electricity.
*Wind farms having clusters of such wind mills are located in coastal regions and in mountain passes where strong and steady winds blow. Windfarms are found in Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, UK, USA and Spain are noted for their wind energy production.
→ Nuclear Power
*Nuclear power is obtained from energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radio active elements like uranium and thorium. These fuels undergo nuclear fission in nuclear reactors and emit power.
*The greatest producers of nuclear power are USA and Europe.
*In India, Rajasthan and Jharkhand have large deposits of Uranium.
*Thorium is found in large quantities in the Monozite sands of Kerala.
*The nuclear power stations in India are located in Kalpakkam in Tamil Nadu, Tarapur in Maharastra, Ranapratap Sagar near Kota in Rajasthan, Narora in Uttar Pradesh and Kaiga in Karnataka.
→ Geothermal Energy
*Heat energy obtained from the earth is called geothermal energy.
*The temperature in the interior of the earth rises steadily as we go deeper.
*Sometimes this heat energy may surface itself in the form of hot springs. This heat energy can be used to generate power.
*Geothermal energy in the form of hot springs has been used for cooking, heating and bathing for several years.
*USA has the world’s largest geothermal power plants followed by New Zealand, Iceland, Philippines and Central America.
*In India, geothermal plants are located in Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh and Puga Valley in Ladakh.
14. Tidal Energy
• Energy generated from tides is called tidal energy. Tidal energy can be harnessed by building dams at narrow openings of the sea.
• During high tide the energy of the tides is used to turn the turbine installed in the dam to produce electricity.
• Russia, France and the Gulf of Kachchh in India have huge tidal mill farms.
15. Biogas
• Organic waste such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung and kitchen waste can be converted into a gaseous fuel called biogas.
• The organic waste is decomposed by bacteria in biogas digesters to emit biogas which is essentially a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide.
• Biogas is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting and produces huge amount of organic manure each year.
16. A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals but without definite composition of constituent of mineral. Rocks from which minerals are mined are known as ores. Although more than 2,800 types of minerals have been identified, only about 100 are considered ore minerals.
17. Switzerland has no known mineral deposit in it.
18. A green diamond is the rarest diamond. The oldest rocks in the world are in Western Australia. They date from 4,300 million years ago, only 300 million years after the earth was formed.
19. The word petroleum is derived from Latin words - Petra meaning rock, oleum meaning oil. So, petroleum means rock oil.
20. Norway was the first country in the world to develop hydroelectricity. The site of the world’s first solar and wind powered bus shelter is in Scotland. The first tidal energy station was built in France.
21. Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Sources of Energy

22. Advantages and Disadvantages of Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
No comments:
Post a Comment