Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Exercise 14.1
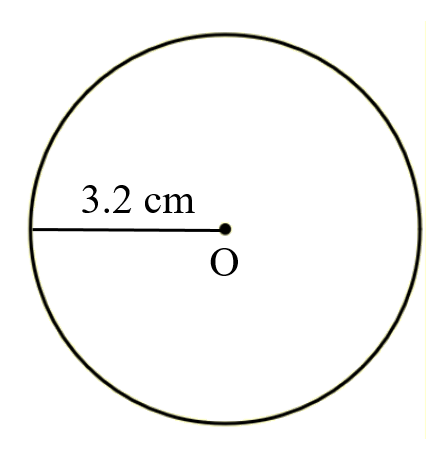
Question 1: Draw a circle of radius 3.2 cm.
Answer:
Given
Circle
Radius 3.2 cm
Rough Figure
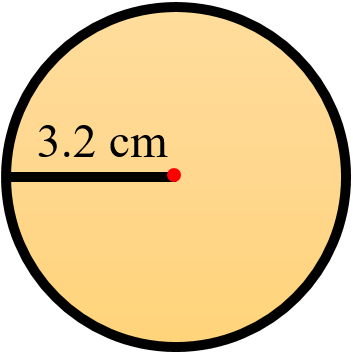
Actual Figure
Steps of Construction
1. Mark a point O anywhere.
2. With O as centre, radius 3.2 cm draw a circle.
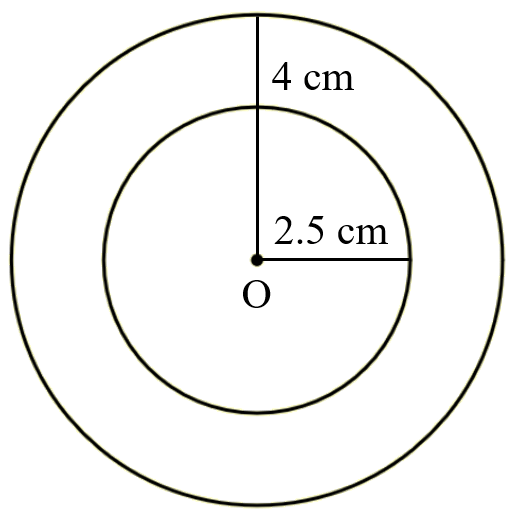
Question 2: With the same centre O, draw two circles of radii 4 cm and 2.5 cm.
Answer:
Given
Circle
Centre O
Radii 4 cm and 2.5 cm
Rough Figure
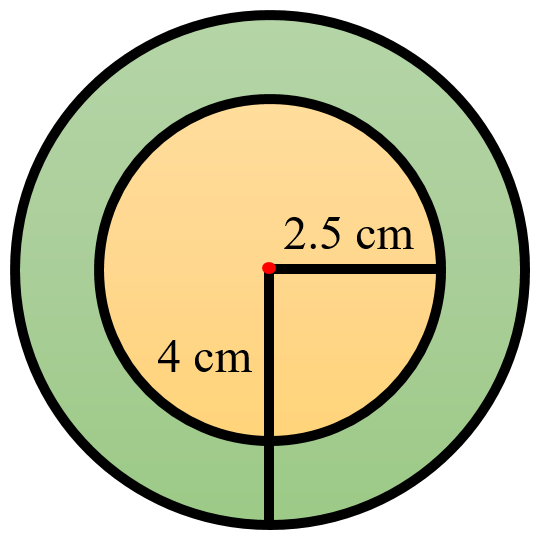
Actual Figure
Steps of Construction
1. Mark a point O anywhere.
2. With O as centre, radius 2.5 cm draw a circle.
3. With O as centre, radius 4 cm draw another circle.
Question 3: Draw a circle and any two of its diameters. If you join the ends of these diameters, what is the figure obtained? What figure is obtained if the diameters are perpendicular to each other? How do you check your answer?
Answer:
i) Draw a circle having its centre ‘O’, also of any radius. Let PR and QS be the two diameters of the circle. A quadrilateral is formed when the ends of PR and QS are joined.
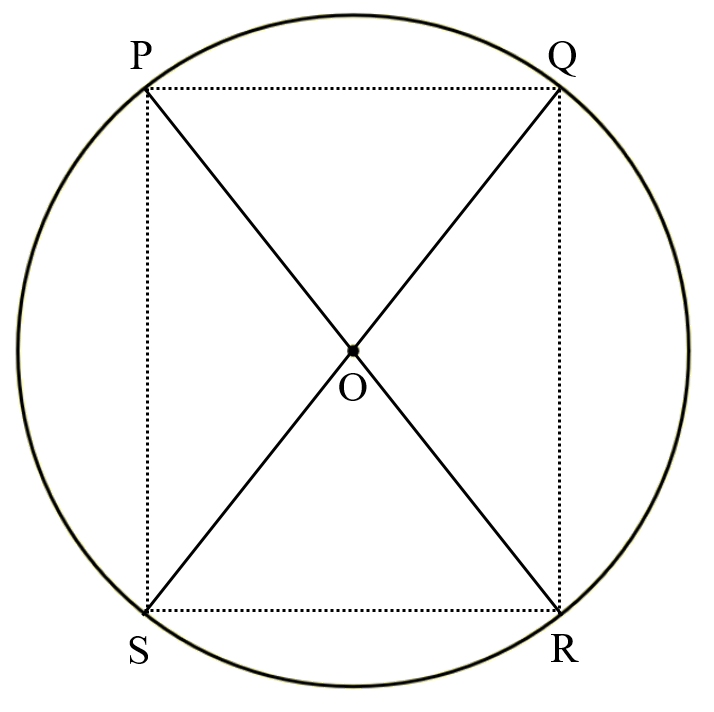
Since, the diameter of a circle are equal in length, quadrilateral that is formed will have its diagonals of equal length. By measuring, PQ = SR and PS = QR. Since, ∠P = ∠Q = ∠R = ∠S = 90°, the PQRS is a rectangle.
ii) Draw a circle having its centre ‘O’, also of any radius. Let PR and QS be the two diameters that are perpendicular to each other in the circle. A quadrilateral is formed when the ends of WY and XZ are joined.
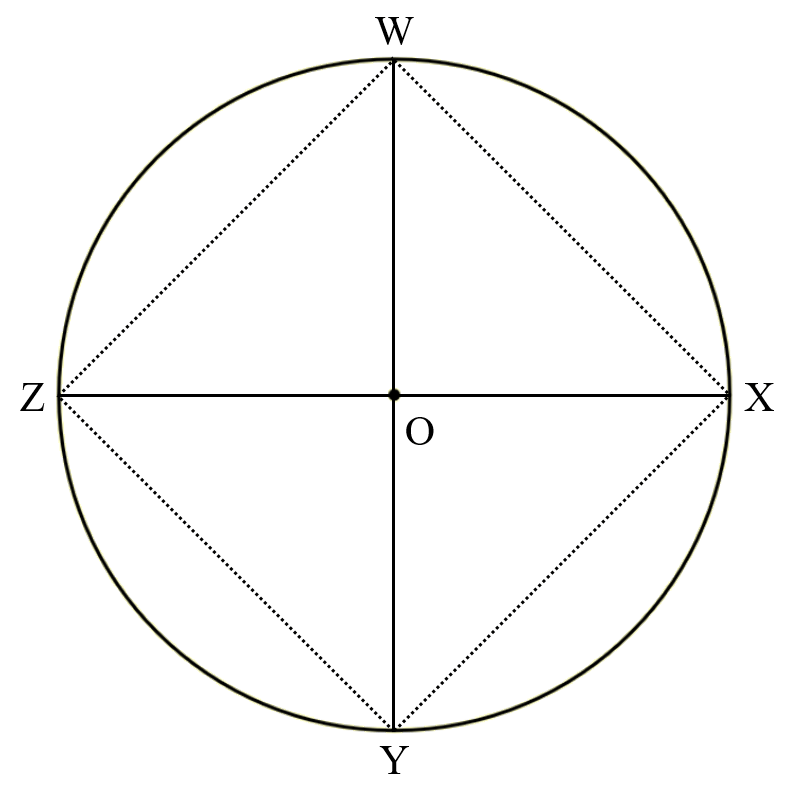
Since, the diameter of a circle are equal in length, quadrilateral that is formed will have its diagonals of equal length. By measuring, WY is perpendicular to XZ, WX = XY = YZ = ZW. Since, ∠W = ∠X = ∠Y = ∠Z = 90°, the WXYZ is a rhombus.
Question 4: Draw any circle and mark points A, B and C such that
a) A is on the circle.
b) B is in the interior of the circle.
c) C is in the exterior of the circle.
Answer:

Question 5: Let A, B be the centres of two circles of equal radii; draw them so that each one of them passes through the centre of the other. Let them intersect at C and D. Examine whether line segment AB and line segment CD are at right angles.
Answer:
Draw two circles having same radius which are passing through the centre of the other circle. The centre of the two circles are A and B and these circle are intersecting at point C and D respectively.
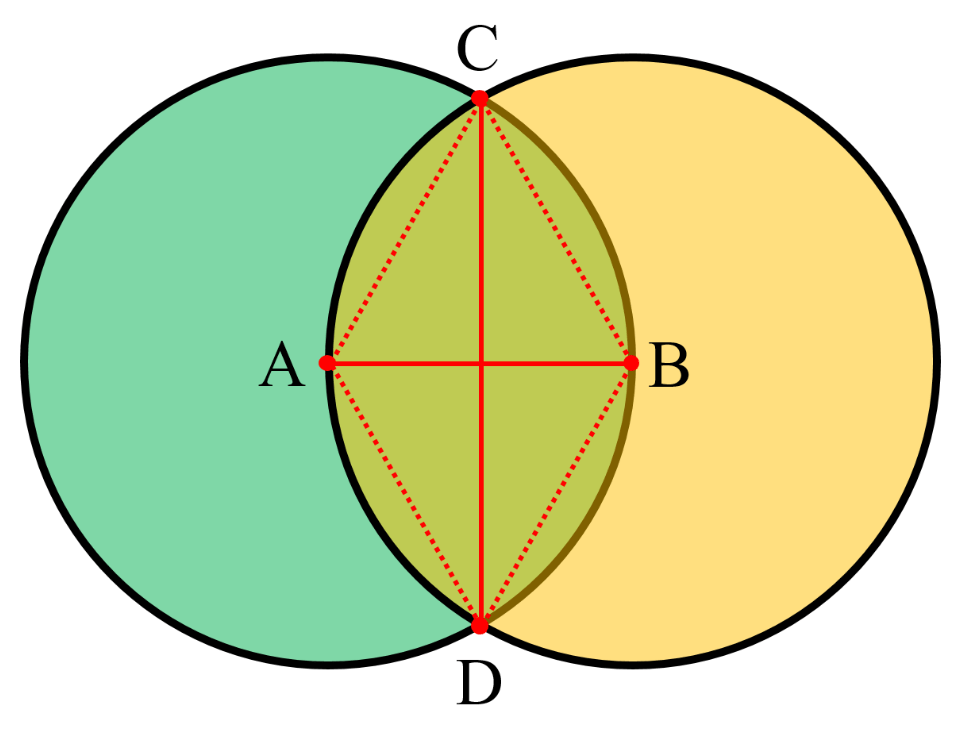
In quadrilateral ABCD,
AD = AC (radius of circle A)
BC = BD (radius of circle B)
Since, radius of both the circles are equal, AC = AD = BC = BD.
Hence, quadrilateral ADBC is a rhombus. The diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at 90°. Therefore, line segments AB and CD are at right angle.
No comments:
Post a Comment