Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire
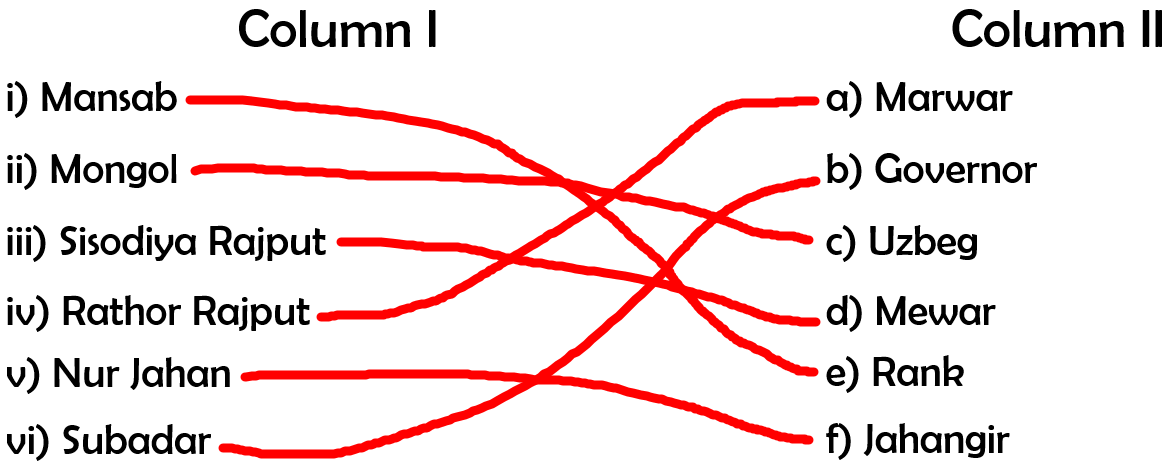
Question 1: Match the following:

Answer:
Question 2: Fill in the blanks:
a) The capital of Mirza Hakim, Akbar’s half-brother, was ____________.
b) The five Deccan Sultanates were Berar, Khandesh, Ahmadnagar, ____________ and _________________.
c) If zat determined a mansabdar’s rank and salary, sawar indicated his ____________.
d) Abul Fazl, Akbar’s friend and counsellor, helped him frame the idea of ____________ so that he could govern a society composed of many religions, cultures and castes.
Answer:
a) The capital of Mirza Hakim, Akbar’s half-brother, was Kabul.
b) The five Deccan Sultanates were Berar, Khandesh, Ahmadnagar, Bijapur and Golconda.
c) If zat determined a mansabdar’s rank and salary, sawar indicated his military responsibility.
d)
Abul Fazl, Akbar’s friend and counsellor, helped him frame the idea of sulh-i kul so that he could govern a society composed of many
religions, cultures and castes.
Question 3: What were the central provinces under the control of the Mughals?
Answer: Delhi, Sindh, Kabul, Mewar, Marwar, Gujarat, Bihar, Bengal, Orissa and Deccan were the central provinces under the control of the Mughals.
Question 4: What was the relationship between the mansabdar and the jagir?
Answer: The mansabdars received their salaries as jagirs (revenue assignment). The mansabdars had the right to collect revenue from a jagir but they could not reside in or administer the jagir.
Question 5: What was the role of the zamindar in Mughal administration?
Answer: The role of zamindars in the Mughal administration was to collect revenue from the peasants. They acted as intermediaries between the rulers and the peasants.
Question 6: How were the debates with religious scholars important in the formation of Akbar's ideas on governance?
Answer: Akbar was interested in the religion and social customs of different people. Akbar’s interaction with people of different faiths made him realise that religious scholars who emphasised ritual and dogma were often bigots. Their teachings created divisions and disharmony amongst his subjects. This eventually led Akbar to the idea of sulh-i kul or “universal peace”. This idea focused on a system of ethics - honesty, justice, peace - that was universally applicable. Abul Fazl helped Akbar in framing a vision of governance around this idea of sulh-i kul. This principle of governance was followed by Jahangir and Shah Jahan as well.
Question 7: Why did the Mughals emphasise their Timurid and not their Mongol descent?
Answer: The Mughal emphasized on their Timurid and not their Mongol descent because Genghis Khan's memory was associated with the massacre of innumerable people. They took pride in Timur because he had captured Delhi in 1398.
Question 8: How important was the income from land revenue to the stability of the Mughal Empire?
Answer: The income from land revenue played an important role in establishing
stability in Mughal empire. It strengthened the economic system of the
empire. The money collected was invested in building forts and for
welfare of subjects. Akbar's revenue minister took a 10-years period to
carry proper calculation of land revenue.
Question 9: Why was it important for the Mughals to recruit mansabdars from diverse backgrounds and not just Turanis and Iranis?
Answer: As the Mughal empire expanded to encompass different regions, it was important for the Mughals to recruit diverse bodies of people in order to make them comfortable. Apart from Turanis and Iranians, they expanded to include Indian Muslims, Afghans, Rajputs, Marathas and other groups.
Question 10: Like the Mughal Empire, India today is also made up of many social and cultural units. Does this pose a challenge to national integration?
Answer: Like the Mughal Empire, India today is also made up of many social and cultural units. This does not pose a challenge to national integration because we've a unified system of government that is democratic and has the same rules and regulations for all the citizens irrespective of religion, etc. India also has a constitution guaranteeing the rights of all
Question 11: Peasants were vital for the economy of the Mughal Empire. Do you think that they are as important today? Has the gap in the income between the rich and the poor in India changed a great deal from the period of the Mughals?
Answer: Peasants were vital for the economy of the Mughal Empire. Peasants are still important today as they were during the Mughal Empire. They cultivate on the land to grow crops without which we cannot survive. They also pay land revenue to the government which is used in various developmental work. Peasants are the backbone of the country.
Question 12: The Mughal Empire left its impact on the different regions of the subcontinent in a variety of ways. Find out if it had any impact in the city, village or region in which you live.
Answer: The Mughal Empire left its impact on the different regions of the subcontinent in a variety of ways. It left great architectural remains of that period which gives lots of information about the construction, materials, styles, etc. Mughal remains are great tourist attractions.
No comments:
Post a Comment