Chapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms Notes
1. The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms.
2. The breakdown of food with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
3. The breakdown of food without using oxygen is called anaerobic respiration.
4. During heavy exercise, fast running, cycling, walking for many hours or heavy weight lifting, the demand for energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Then anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscle cells to fulfil the demand of energy.
5. Hot water bath or massage improves circulation of blood. As a result, the supply of oxygen to the muscle cells increases. The increase in the supply of oxygen results in the complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water.
6. Breathing means taking in air rich in oxygen and giving out air rich in carbon dioxide with the help of respiratory organs.
7. The taking in of air rich in oxygen into the body is called inhalation.
8. The giving out of air rich in carbon dioxide is known as exhalation.
9. The number of times a person breathes in a minute is termed as the breathing rate.
10. During breathing inhalation and exhalation take place alternately. A breath means one inhalation plus one exhalation.
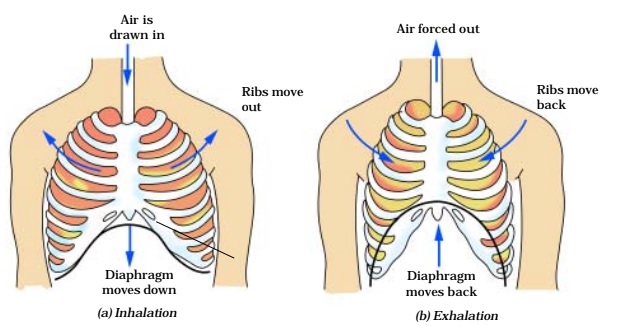
11. When we inhale air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe. Lungs are present in the chest cavity. This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides. A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage.
12. During inhalation, ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves down. This movement increases space in our chest cavity and air rushes into the lungs. The lungs get filled with air. During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position. This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed out of the lungs.
13. A cockroach has small openings on the sides of its body called spiracles. Insects have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles. These air tubes or tracheae are found only in insects and not in any other group of animals.
14. The earthworms breathe through their skins. The skin of an earthworm feels moist and slimy on touching. Gases can easily pass through them. Though frogs have a pair of lungs like human beings, they can also breathe through their skin, which is moist and slippery.
15. In plants, the roots take in air present in the soil. Leaves have tiny pores called stomata through which they exchange gases. The breakdown of glucose in the plant cells is similar to that in other living beings.
16. Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They respire anaerobically and during this process yield alcohol. They are, therefore, used to make wine and beer.
17. On an average, an adult human being at rest breathes in and out 15 - 18 times in a minute. During heavy exercise, the breathing rate can increase up to 25 times per minute. While we exercise, not only do we breathe fast, we also take deep breaths and thus inhale more oxygen.
18. Smoking damages lungs. Smoking is also linked to cancer. It must be avoided.
19. The air around us has various types of unwanted particles, such as smoke, dust, pollens, etc. When we inhale, the particles get trapped in the hair present in our nasal cavity. However, sometimes these particles may get past the hair in the nasal cavity. Then they irritate the lining of the cavity, as a result of which we sneeze. Sneezing expels these foreign particles from the inhaled air and a dust-free, clean air enters our body. When you sneeze, you should cover your nose so that the foreign particles you expel are not inhaled by other persons.
20. Aerobic Respiration formula
21. Anaerobic Respiration formula
22.
23. The percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in inhaled and exhaled air.
24.Mechanism of breathing in human beings




No comments:
Post a Comment