Chapter 11 Mensuration Exercise 11.3
Question 1: There are two cuboidal boxes as shown in the adjoining figure. Which box requires the lesser amount of material to make?

Answer:
Given
2 cuboidal boxes
Box A
l = 60 cm
b = 40 cm
h = 50 cm
Box B
l = 50 cm
b = 50 cm
h = 50 cm
To find
Which box requires lesser amount of material to make?
Formula
TSA of cuboid (Box A)= 2(lh + bh + lb)
TSA of cube (Box B) = 6s²
Working
Box A
= 2[(60)(50) + (40)(50) + (60)(40)]
= 2[3000 + 2000 + 2400]
= 2[7400]
= 14800 cm²
Box B
= 6 × (50)²
= 6 × 2500
= 15000 cm²
Comparing
15000 cm² > 14800 cm²
Therefore, Box A requires lesser amount of material to make.
Question 2: A suitcase with measures 80 cm × 48 cm × 24 cm is to be covered with a tarpaulin cloth. How many metres of tarpaulin of width 96 cm is required to cover 100 such suitcases?
Answer:
Given
Number of suitcases = 100
Length of suitcase = 80 cm
Breadth of suitcase = 48 cm
Height of suitcase = 24 cm
Width of tarpaulin cloth = 96 cm
To find
Length of cloth required to cover 100 suitcases
Formula
TSA = 2(lh + bh + lb)
Area of cloth = l × b
Working
= 2[(80)(24) + (48)(24) + (80)(48)]
= 2[1920 + 1152 + 3840]
= 2[6912]
= 13824 cm²
Length of cloth required for 1 suitcase = ?
= 13824 = l × 96
= l = 13824/96
= l = 144 cm
Length of cloth required for 100 suitcase = ?
= 144 × 100
= 14400 cm
= 144 m
Therefore, 144 metres of tarpaulin of width 96 cm is required to cover 100 such suitcases
Question 3: Find the side of a cube whose surface area is 600 cm².
Answer:
Given
TSA of cube = 600 cm²
To find
Side of the cube
Formula
TSA of cube = 6s²
Working
= 600 = 6s²
= s² = 600/6
= s² = 100
= √100
= s = 10 cm
Therefore, the side of cube whose surface area is 600 cm² is 10 cm.
Question 4: Rukhsar painted the outside of the cabinet of measure 1 m × 2 m × 1.5 m. How much surface area did she cover if she painted all except the bottom of the cabinet?

Answer:
Given
Cuboidal cabinet
length = 1 m
breadth = 2 m
height = 1.5 m
To find
Surface area to be painted except the bottom
Formula
LSA + area of top = 2h(l + b) + lb
or
TSA - area of bottom
2(lh + bh + lb) - lb
Working
= 2 × 1.5(1+ 2) + 1 × 2
= 3 × 3 + 2
= 11 m²
Therefore, 11 m² of cabinet she has painted all except the bottom of the cabinet.
Question 5: Daniel is painting the walls and ceiling of a cuboidal hall with length, breadth and height of 15 m, 10 m and 7 m respectively. From each can of paint 100 m² of area is painted. How many cans of paint will she need to paint the room?
Answer:
Given
Dimensions of room
length = 15 m
breadth = 10 m
height = 7 m
Area painted by each can = 100 m²
To find
Number of paint cans used
Formula
LSA + area of ceiling = 2h(l + b) + lb
or
TSA - area of floor = 2(lh + bh + lb) - lb
Working
= 2 × 7(15 + 10) + 15 × 10
= 14 × 25 + 150
= 350 + 150
= 500 m²
Number of cans required = ?
= 500/100
= 5 cans
Therefore, she would need 5 paint cans to paint the room.
Question 6: Describe how the two figures at the right are alike and how they are different. Which box has larger lateral surface area?
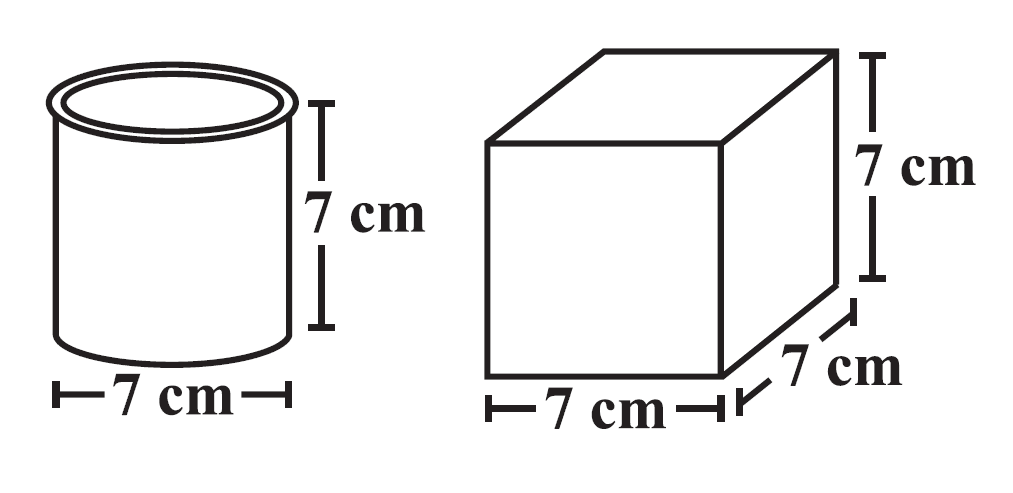
Answer:
Similarities
→ Both have the same height.
Differences
→ The first one is a cylinder while the second one is cube.
→ Both have a different LSA. The cube has a larger one.
Cylinder LSA = 2πrh
= 2 × 22/7 × 3.5 × 7
= 2 × 22 × 3.5
= 154 cm²
Cube LSA = 4s²
= 4 × 7²
= 4 × 49
= 196 cm²
Question 7: A closed cylindrical tank of radius 7 m and height 3 m is made from a sheet of metal. How much sheet of metal is required?
Answer:
Given
Closed cylindrical tank
radius = 7 m
height = 3 m
To find
Sheet of metal required to make the tank
Formula
TSA of cylinder = 2πr(h + r)
Working
= 2 × 22/7 × 7 × (3 + 7)
= 2 × 22 × 10
= 440 m²
Therefore, the sheet of metal required to make the closed cylindrical tank is 440 m².
Question 8: The lateral surface area of a hollow cylinder is 4224 cm². It is cut along its height and formed a rectangular sheet of width 33 cm. Find the perimeter of rectangular sheet?
Answer:
Given
Hollow cylinder LSA = 4224 cm²
Width of rectangular sheet = 33 cm
To find
Perimeter of the rectangular sheet
Formula
LSA of cylinder = 2πrh
Area of rectangle = l × b
Perimeter of rectangle = 2(l + b)
Working
LSA of cylinder = area of rectangle
4224 = l × 33
l = 4224/33
l = 128 cm
Perimeter of rectangle = ?
= 2(l + b)
= 2(128 + 33)
= 2 × 161
= 322 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangular sheet is 322 cm.
Question 9: A road roller takes 750 complete revolutions to move once over to level a road. Find the area of the road if the diameter of a road roller is 84 cm and length is 1 m.
Answer:
Given
Road roller
diameter = 84 cm
height = 1 m (100 cm)
Number of revolutions = 750
To find
The area of road
Formula
LSA of cylinder = 2πrh
Working
Area of road = ?
= 750 × 2πrh
= 750 × 2 × 22/7 × 42 × 100
= 750 × 2 × 22 × 6 × 100
= 19800000 cm²
(1 m² = 10000 cm²)
= 19800000/10000
= 1980 m²
Therefore, the area of the road is 1980 m².
Question 10. A company packages its milk powder in cylindrical container whose base has a diameter of 14 cm and height 20 cm. Company places a label around the surface of the container (as shown in the figure). If the label is placed 2 cm from top and bottom, what is the area of the label.

Answer:
Given
Cylindrical container
diameter = 14 cm
height = 20 cm
Label is placed 2 cm from top and bottom
To find
Area of label
Formula
LSA of cylinder = 2πrh
Working
(height of label is 16 cm because 2 cm from top and bottom are excluded so 20 - 4 = 16 cm)
= 2 × 22/7 × 7 × 16
= 2 × 22 × 16
= 704 cm²
Therefore, the area of label is 704 cm².
No comments:
Post a Comment