Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.1
Question 1: What is the disadvantage in comparing line segments by mere observation?
Answer: By mere observation, we can’t compare the line segments with slight difference in their length. We can’t say which line segment has greater length. So, the errors may happen due to improper viewing.
Question 2: Why is it better to use a divider than a ruler, while measuring the length of a line segment?
Answer: When we use a ruler, chances of error may occur because of the thickness of the ruler and angular viewing. So, if we use divider it will give the accurate measurement.
Question 3: Draw any line segment, say AB. Take any point C lying in between A and B. Measure the lengths of AB, BC and AC. Is AB = AC + CB? [Note: If A, B, C are any three points on a line such that AC + CB = AB, then we can be sure that C lies between A and B.]
Answer:
Since, point C is lying in between A and B
AB = AC + CB
Example:
AB is a line segment of length 10 cm and C is a point between A and B such that AC = 4 cm and CB = 6 cm.
AC + CB = 10 cm
4 cm + 6 cm = 10 cm
10 cm = 10 cm
Therefore, AB = AC + CB has been proved.
Question 4: If A, B, C are three points on a line such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm and AC = 8 cm, which one of them lies between the other two?
Answer:
Given
AB = 5 cm
BC = 3 cm
AC = 8 cm
Comparing AB, BC and AC, AC is the longest side.
= 8 cm = 5 cm + 3 cm
= AC = AB + BC
Therefore, the point B lies between A and C.
Question 5: Verify, whether D is the midpoint of AG.

Answer: Yes, D is the midpoint of AG because it is located 3 units away from A and 3 units away from G.
Question 6: If B is the midpoint of AC and C is the midpoint of BD, where A, B, C, D lie on a straight line, say why AB = CD?
Answer:

B is the midpoint of AC. So AB = BC. (Equation 1)
C is the midpoint of BD. So BC = CD. (Equation 2)
From equation 1 and equation 2
AB = CD
Hence, verified.
Question 7: Draw five triangles and measure their sides. Check in each case, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is always less than the third side.
Answer:
Triangle 1 ABC
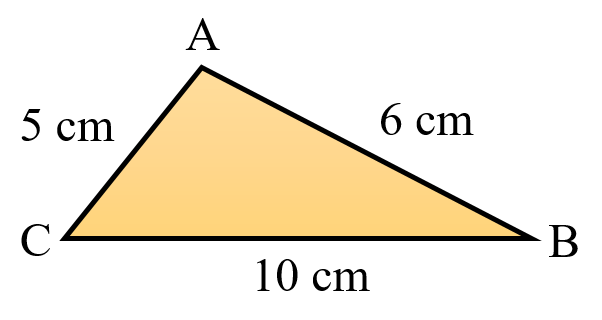
AB = 6 cm
BC = 10 cm
AC = 5 cm
AC + AB = 6 cm + 5 cm = 11 cm
Comparing
11 cm > 10 cm
AB + AC > BC
Therefore, the sum of the lengths of any two sides in always greater than the third side.
Triangle 2 PEA
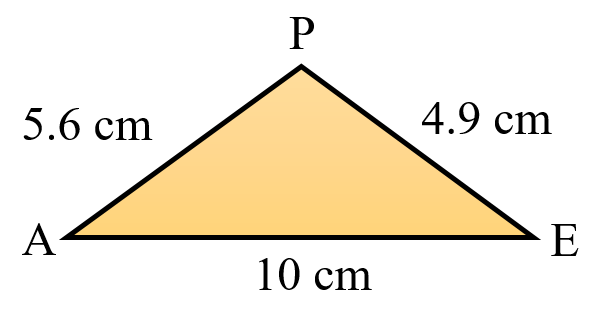
PE = 4.9 cm
EA = 10 cm
PA = 5.6 cm
PA + PE = 4.9 cm + 5.6 cm = 10.5 cm
Comparing
10.5 cm > 10 cm
PA + PE > AE
Therefore, the sum of the lengths of any two sides in always greater than the third side.
Triangle 3 WTP
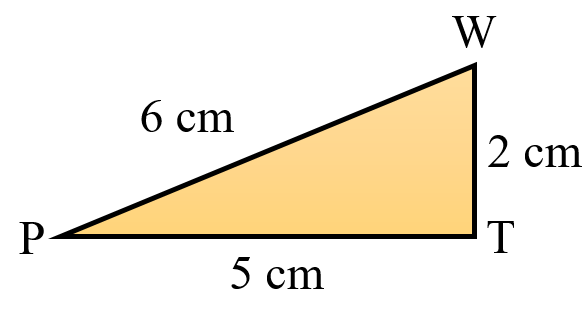
WP = 6 cm
WT = 2 cm
PT = 5 cm
WT + TP = 5 cm + 2 cm = 7 cm
Comparing
7 cm > 6 cm
WT + TP > WP
Therefore, the sum of the lengths of any two sides in always greater than the third side.
Triangle 4 MAP
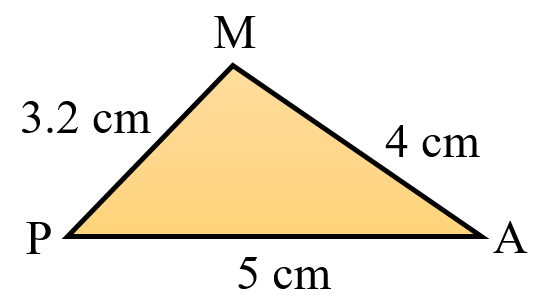
MA = 4 cm
MP = 3.2 cm
PA = 5 cm
MA + MP = 4 cm + 3.2 cm = 7.2 cm
Comparing
7.2 cm > 5 cm
MP + MA > PA
Therefore, the sum of the lengths of any two sides in always greater than the third side.
Triangle 5 TEA

ET = 9 cm
TA = 10 cm
EA = 3 cm
EA + TA = 10 cm + 3 cm = 13 cm
Comparing
13 cm > 9 cm
TA + EA > ET
Therefore, the sum of the lengths of any two sides in always greater than the third side.
No comments:
Post a Comment